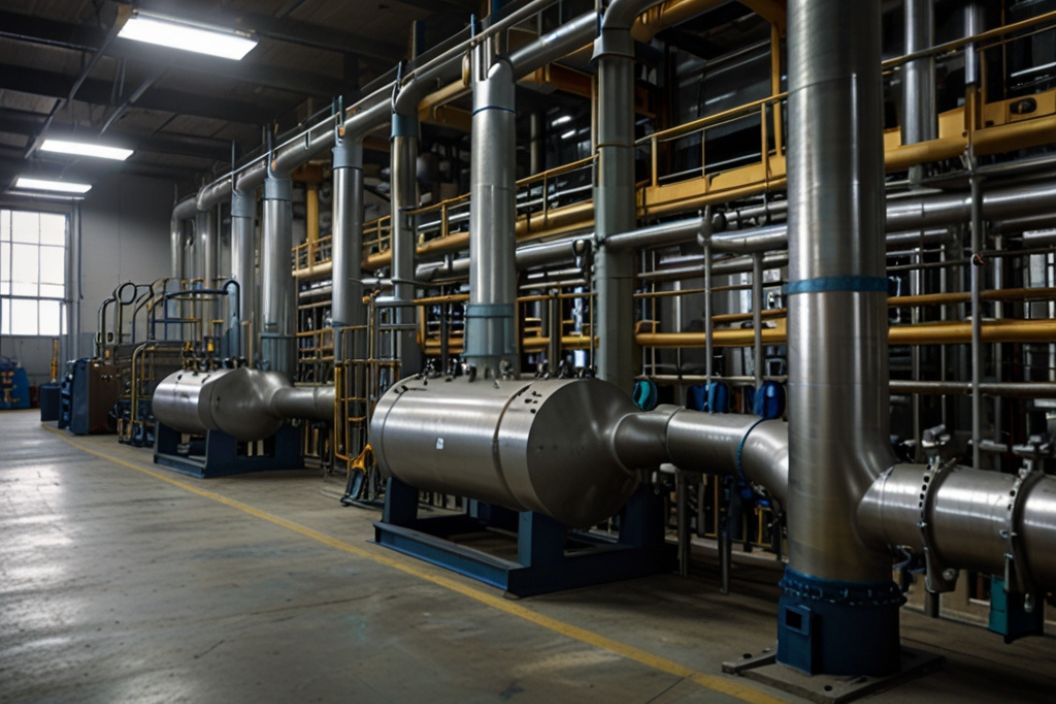
The chemical process industry (CPI) is a cornerstone of modern society, providing the essential building blocks for a wide array of products we use daily. From the plastics in our electronics to the pharmaceuticals that keep us healthy, the CPI plays a crucial role in transforming raw materials into finished products. In this blog, we’ll explore the journey of these materials through the chemical process industry, delving into the various stages, technologies, and innovations that make it all possible.
The Importance of the Chemical Process Industry
The CPI is a major driver of economic growth, employing millions of people worldwide and generating trillions of dollars in revenue. It encompasses a diverse range of sectors, including petrochemicals, agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and specialty chemicals. The industry not only supports other industries by providing essential materials but also plays a key role in advancing technology and sustainability.
The Journey from Raw Materials to Finished Products
1. Extraction and Preparation of Raw Materials
The journey begins with the extraction of raw materials from natural sources. These materials can be broadly categorized into:
- Minerals and Metals: Extracted through mining operations, these materials are used in various chemical processes.
- Petroleum and Natural Gas: Obtained through drilling, these hydrocarbons serve as the primary feedstocks for many chemical processes.
- Biological Materials: Sourced from plants and animals, these materials are increasingly used in bio-based chemical processes.
Once extracted, these raw materials undergo initial preparation steps, such as crushing, grinding, and purification, to make them suitable for further processing.
2. Chemical Reactions and Synthesis
The heart of the CPI lies in chemical reactions and synthesis processes. These processes transform raw materials into intermediate and final products through various chemical reactions. Key technologies and methods used in this stage include:
- Catalysis: Catalysts are substances that speed up chemical reactions without being consumed. They are crucial in increasing the efficiency of chemical processes.
- Polymerization: This process combines small molecules (monomers) into large, complex molecules (polymers), which form the basis of plastics, synthetic fibers, and rubbers.
- Fermentation: Used in the production of bio-based chemicals, fermentation involves using microorganisms to convert organic materials into chemicals like ethanol and acetic acid.
- Distillation and Separation: These processes are used to separate and purify the products of chemical reactions, ensuring the final products meet the required specifications.
3. Formulation and Processing
After the initial chemical synthesis, the intermediate products often undergo further processing to achieve the desired properties and functionality. This stage involves:
- Blending and Mixing: Combining different chemicals to create products with specific characteristics.
- Extrusion and Molding: Used in the plastics industry to shape materials into final products like bottles, pipes, and films.
- Coating and Surface Treatment: Applying coatings to materials to enhance properties like corrosion resistance, adhesion, and appearance.
4. Quality Control and Testing
Ensuring the quality and safety of chemical products is paramount. Throughout the production process, rigorous quality control measures are implemented. This includes:
- Analytical Testing: Using advanced techniques like chromatography and spectroscopy to analyze the composition and purity of products.
- Performance Testing: Evaluating the performance characteristics of products to ensure they meet industry standards and customer requirements.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring that products comply with relevant regulations and safety standards, such as REACH in Europe and TSCA in the United States.
5. Packaging and Distribution
The final stage in the journey from raw materials to finished products is packaging and distribution. This involves:
- Packaging: Designing and producing packaging that protects the product, ensures safety, and provides necessary information to consumers.
- Logistics: Efficiently managing the transportation and distribution of products to ensure they reach customers in good condition and on time.
Innovations and Trends in the Chemical Process Industry
The CPI is continually evolving, driven by technological advancements and a growing focus on sustainability. Some key innovations and trends include:
1. Green Chemistry and Sustainability
Green chemistry principles are being increasingly adopted to reduce the environmental impact of chemical processes. This includes using renewable feedstocks, reducing waste, and developing energy-efficient processes.
2. Digitalization and Industry 4.0
The integration of digital technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics, is transforming the CPI. These technologies enhance process efficiency, improve product quality, and enable predictive maintenance.
3. Biotechnology and Bio-based Chemicals
Biotechnology is playing a growing role in the CPI, with bio-based chemicals offering a sustainable alternative to traditional petrochemicals. Advances in genetic engineering and fermentation technology are driving this shift.
4. Advanced Materials
The development of advanced materials, such as nanomaterials and smart materials, is opening new possibilities in various industries. These materials offer enhanced properties and functionalities, driving innovation in product design and performance.
Conclusion
The chemical process industry is a dynamic and vital sector that underpins modern society. From the extraction of raw materials to the production of finished products, the CPI involves complex processes and cutting-edge technologies. As the industry continues to innovate and embrace sustainable practices, it will play an increasingly important role in addressing global challenges and driving economic growth.
By understanding the journey from raw materials to finished products, we can appreciate the critical role the CPI plays in our lives and the ongoing efforts to make it more sustainable and efficient.